Statistics reveal that approximately 866 million metric tons of carbon dioxide are stored in U.S. forests alone. But unfortunately, the lungs of our planet are under constant siege. From microscopic fungi to invasive insects, these threats are ever-present and can have devastating effects.
The fight against tree diseases is a complex one. It’s a battle that involves understanding the intricacies of each disease and implementing effective treatment plans. Prevention, early detection, and proper management are the first line of defense.
As tree lovers, we all have a role in preserving and protecting these large, silent life forms that enrich our world in countless ways. Therefore, in this guide, we’ll discuss how to treat tree disease and the steps you need to take to combat them effectively.

Identifying Tree Diseases
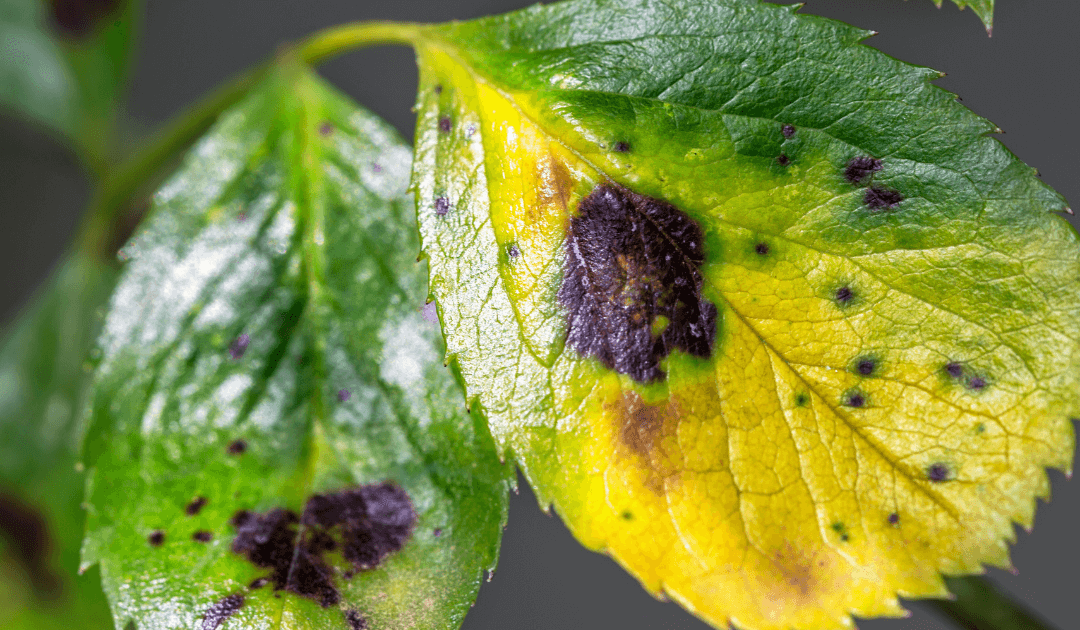
The first step towards disease control is correctly identifying the signs of an infected tree. Symptoms can range from leaf spots and dying branches to changes in fruiting structure.
However, accurate tree disease diagnosis often requires professional tree service due to the complexity of various diseases and their symptoms.
For instance, Dutch elm disease might manifest as yellowing leaves, while apple scab presents as velvety, dark brown splotches on apple trees’ leaves and fruits.
General Signs To Look For: There are general signs that indicate a tree may be diseased. Unusual leaf discoloration, premature leaf drop, stunted growth, or the presence of pests are red flags.
Bark abnormalities such as cracks, peeling, or unusual growths can also signify trouble. Remember, each tree is unique, and symptoms can vary.
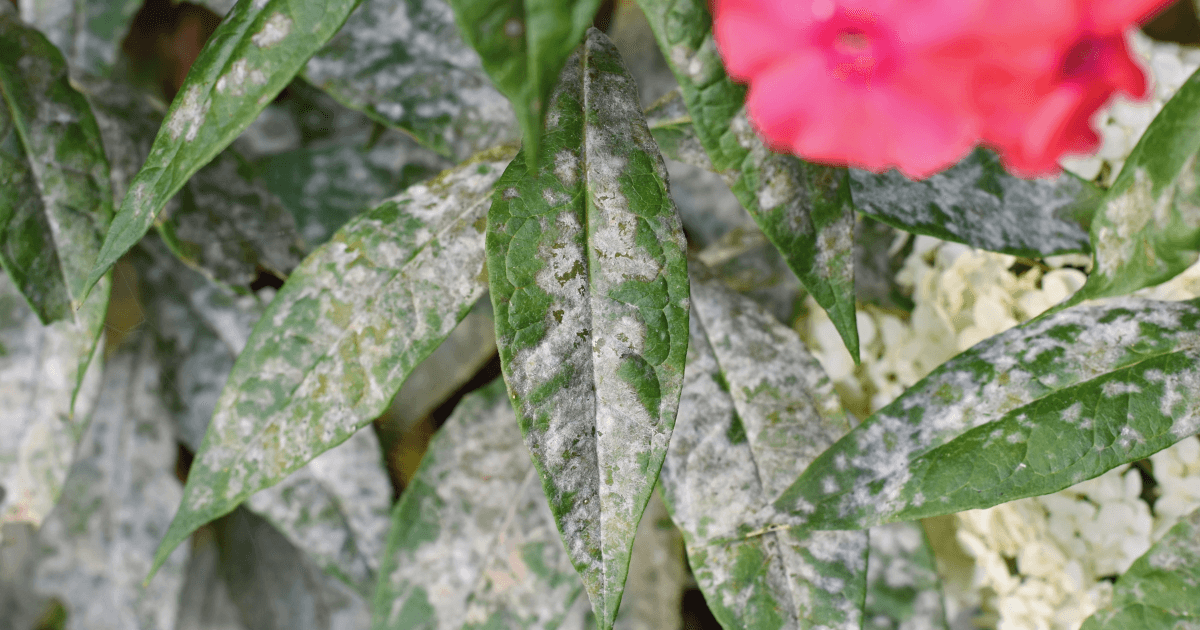
Fungal Tree Diseases
Fungal diseases are some of the most common tree diseases. Here are a few you should be aware of:
- Dutch Elm Disease: A fungal infection that blocks water transport in the tree, leading to wilting and eventually dying. It spreads through the air and by beetles.
- Cedar Apple Rust: This disease affects both cedar and apple trees, causing rust-colored lesions on leaves and fruits.
- Oak Wilt: Caused by a fungus that blocks the tree’s water transport system, this disease results in rapid leaf shedding and death.
- Powdery Mildew: Characterized by white, powdery fungal spores on leaves, this disease thrives in wet weather but can be controlled with fungicide treatment.
- Root Rot: A fungal disease that attacks tree roots, causing decay and destabilization.
- Diplodia Tip Blight: A common fungal disease in pines, this infection causes needle browning and tree death if left untreated.
Bacterial Tree Diseases
Bacteria can also cause serious harm to trees. Some bacterial diseases include:
- Fire Blight: This disease affects fruit trees, especially apple and crabapple trees, resulting in burned-looking branches and wilted flowers.
- Bacterial Leaf Scorch: This disease causes browning and scorching leaf edges in shade trees like oak and elm.
- Canker Diseases: These cause sunken, dead areas on tree branches or trunks, often leading to structural weakness and breakage.
- Lethal Yellowing: Primarily affecting palm trees, this bacterial disease results in yellowing and death of the tree’s crown, leaving behind a bare trunk.
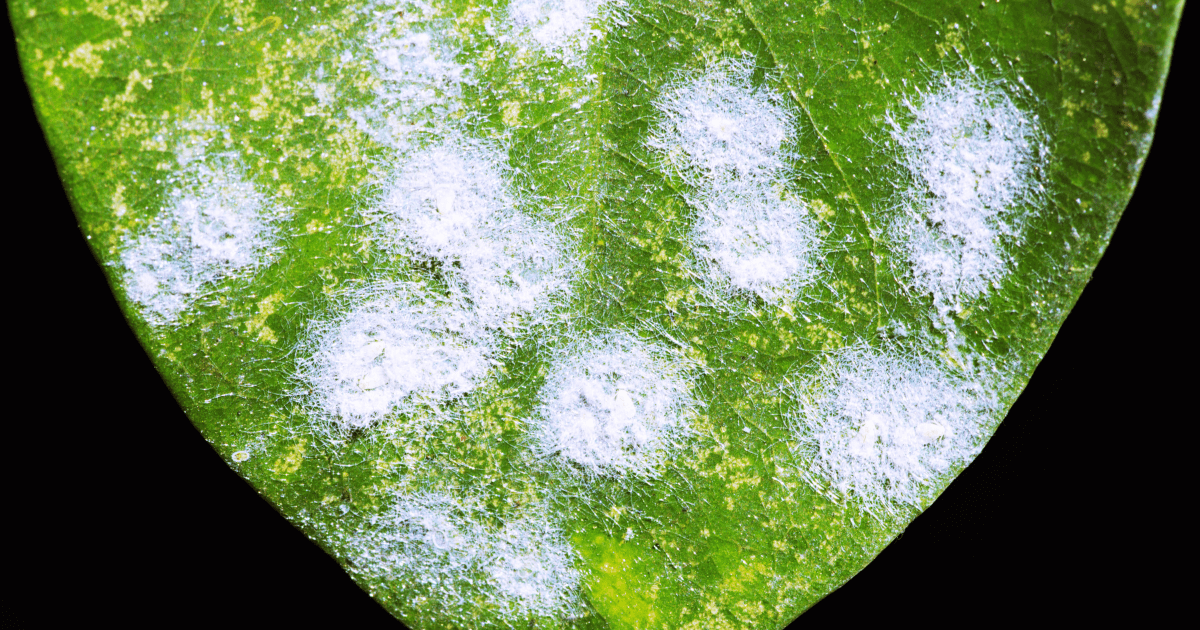

Viral Tree Diseases
Viral diseases in trees are less common than bacterial or fungal diseases, but they can still cause significant damage. Here are some you should be aware of:
- Mosaic Virus: This disease affects several species of trees and shrubs, causing a mottled or mosaic pattern on leaves.
- Apple Stem Grooving Virus: This viral disease leads to grooves along the stems and branches of apple trees, impacting their overall health.
- Ash Yellows: A fatal viral infection that causes stunted growth and discoloration of ash tree leaves.
- Cherry Leaf Roll Virus: A common virus that causes wrinkled, rolled-up leaves on cherry trees.
Non-Infectious Tree Diseases
Non-infectious diseases are usually caused by adverse weather conditions, poor soil conditions, or other environmental factors rather than a specific fungal or bacterial pathogen. Some common non-infectious diseases include:
- Leaf Scorch: This is often caused by hot, dry weather conditions, resulting in browned and shriveled leaves.
- Chlorosis: A condition caused by nutrient deficiency, particularly iron, resulting in yellowing leaves.
- Crown Thinning: Often a result of stressed trees due to poor soil conditions or drought, leading to leaff bisparse foliage.
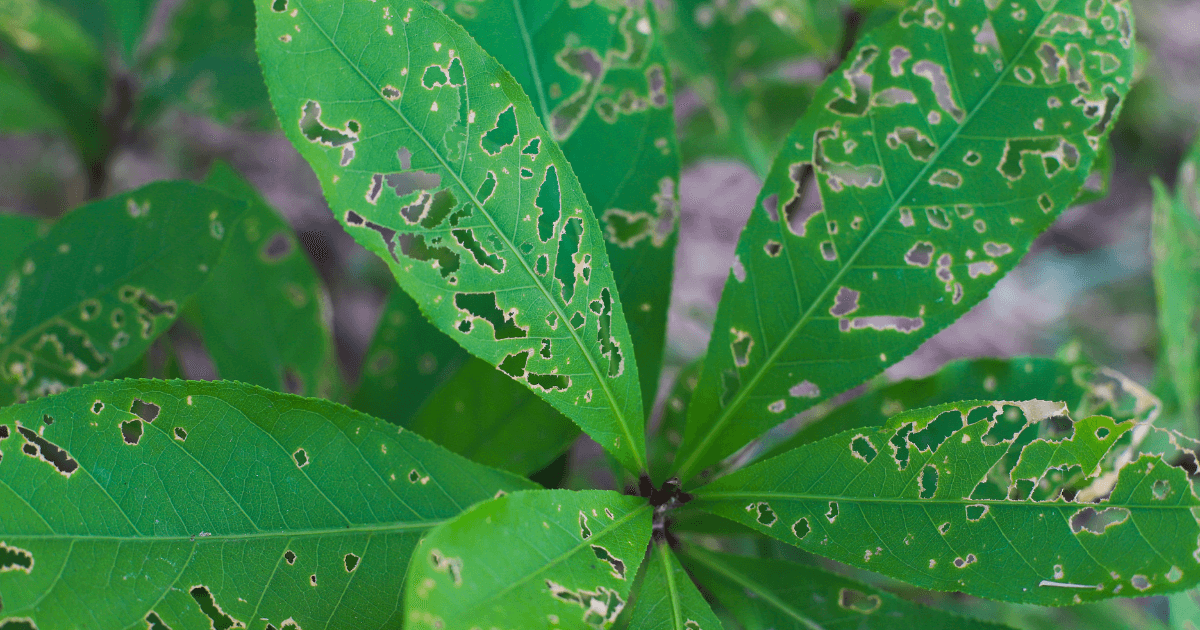
Insect Infestations
Insects can also attack trees, causing significant damage. Some of the most notorious tree pests include:
- Emerald Ash Borer: An invasive beetle that feeds on ash trees and has caused widespread devastation in North America.
- Oak Processionary Moth: The larvae of this moth feed on oak leaves, causing defoliation and weakening the tree’s health.
- Gypsy Moth: This moth can defoliate entire forests, leaving trees vulnerable to secondary infections and death.
Preventing Tree Diseases
One of the best ways to prevent common tree diseases is by maintaining proper care and attention. Regularly inspect your trees for any signs of disease or insect infestation. Pay close attention to the tree roots, branches, and leaves.
Another preventive measure is ensuring good air circulation around your trees. This can help to ward off fungal diseases like powdery mildew and canker diseases, which often thrive in damp conditions. Also, consider pre-emptive foliar treatments in early spring to keep your trees healthy.
Watering practices are also crucial. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering can stress trees, making them more susceptible to disease. Balance is key.
Lastly, remember that healthy soil conditions are vital for healthy plants. Test your soil regularly to ensure it has the necessary nutrients and pH balance for your specific tree species.
Tree Disease Diagnosis
Diagnosing tree diseases can be tricky, as many diseases share similar symptoms like leaf spots, dying branches, and discoloration. However, accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment.
Here are some steps to help you diagnose tree diseases:
- Observe the symptoms: Take a closer look at your tree and note any unusual changes in its appearance, such as discolored leaves or dying branches.
- Identify the affected area: Some diseases may only affect certain parts of the tree, like the crown or roots.
- Research tree diseases: Use reliable resources to identify common diseases that may affect your tree species.
- Consult a professional: If you’re unsure or need a second opinion, consider consulting an arborist or horticulturist for accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
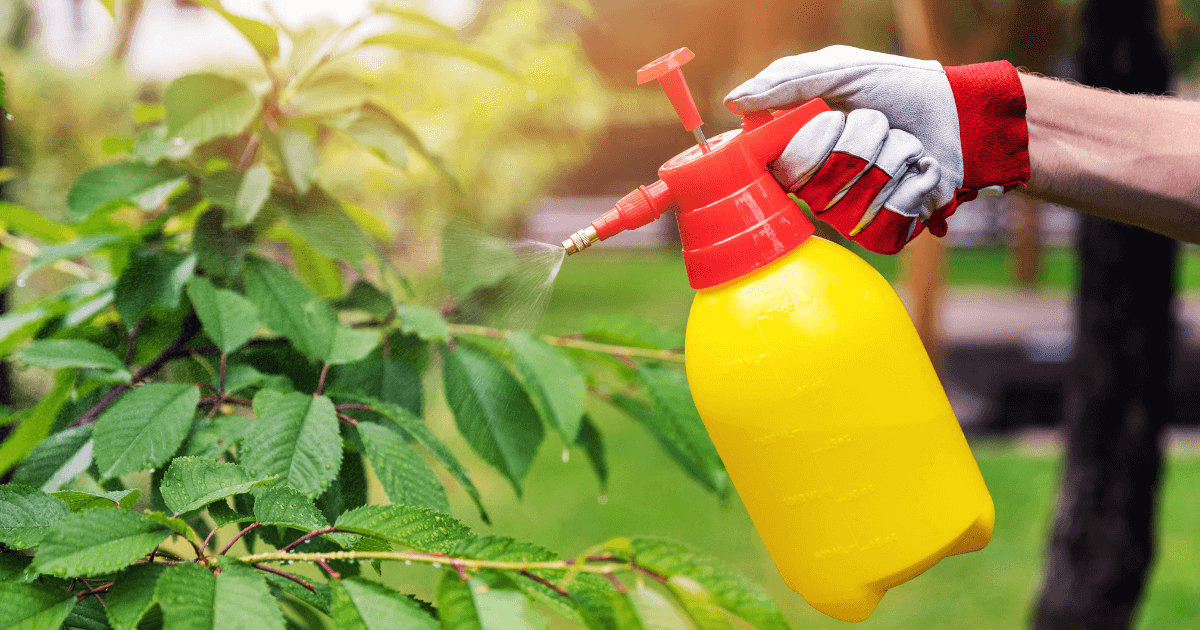

Treatment and Management Options
Once a diagnosis is made, the next step is tree disease treatment. Here are some options:
- Fungicide Treatments: For fungal infections like apple scab or cedar apple rust, fungicides can be an effective treatment. Remember, timing is crucial for these treatments to work effectively.
- Pruning: Infected branches should be pruned to prevent the spread of disease. Always clean your tools after pruning a diseased tree.
- Soil Treatments: For diseases affecting tree roots, soil treatments can help. These might include changing watering practices or adding nutrients to the soil.
- Insect Control: Some diseases are spread by insects. In these cases, controlling the insect population can help control the disease.
- Cultural Practices: This includes proper watering, mulching, and ensuring good air circulation.
Cultural Practices for Healthy Trees
Cultural practices are crucial in maintaining tree health and preventing tree diseases. These include:
- Proper Watering: Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering can stress trees, making them more susceptible to disease.
- Nutrient Management: Ensuring your soil has the necessary nutrients is vital for healthy trees. Regular soil testing can help manage nutrient levels effectively.
- Good Air Circulation: Proper spacing between trees can prevent fungal infections like powdery mildew and canker diseases, which often thrive in damp conditions.
- Mulching: This helps maintain moisture levels, control weeds, and protect tree roots.
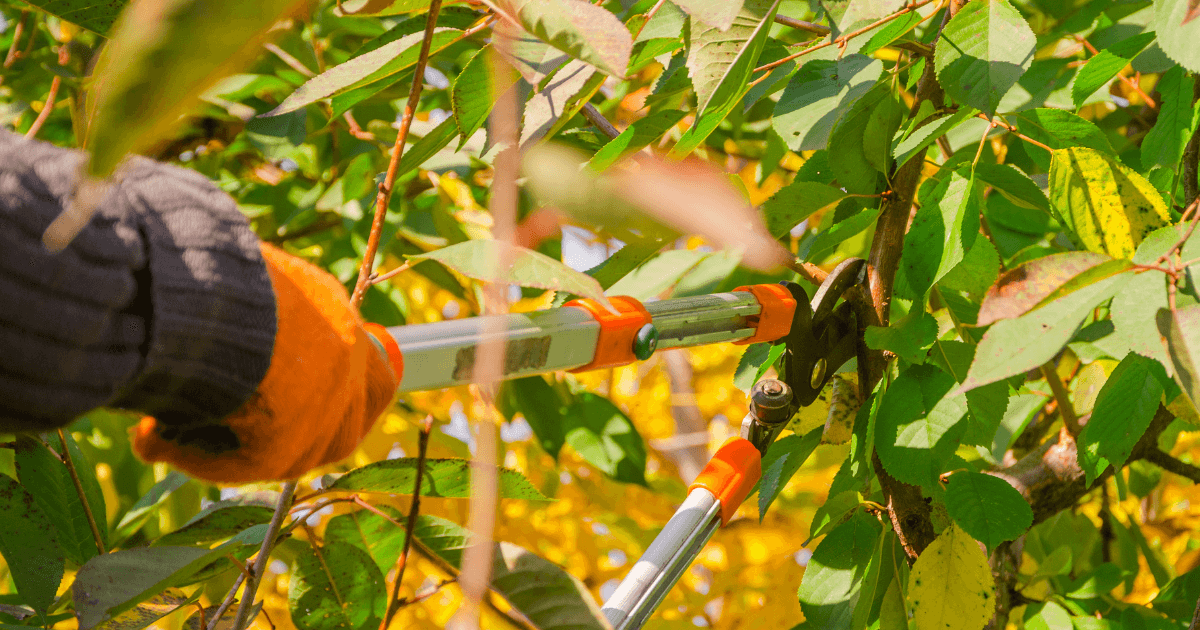

Pruning and Trimming
Pruning and trimming are essential for maintaining the health of your trees. Removing diseased branches can prevent the spread of specific diseases. Always clean your tools after pruning an infected tree to avoid spreading the disease to other trees.
Regular pruning can also improve air circulation and sunlight penetration, which promotes tree health and can help prevent fungal diseases.
Chemical Treatments
Chemical treatments, such as fungicides, can be effective in treating certain fungal diseases like apple scab and cedar apple rust. However, these treatments should be used judiciously and according to label instructions to avoid harming beneficial insects or the environment. Always read and follow the label instructions carefully.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance can go a long way towards keeping your trees healthy and free from disease. Here are some pointers:
- Check trees regularly for signs of disease or insect infestation.
- Schedule regular pruning and trimming to remove dead or diseased branches.
- Monitor soil conditions and adjust watering practices as needed.
- Apply preventive treatments in early spring to ward off common diseases.
- Consult a professional tree service if you notice any unusual symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how to treat tree disease is integral to maintaining a healthy, vibrant landscape. Regular inspections, appropriate watering, soil testing, and preventive treatments are all crucial steps. Employing effective cultural practices, such as appropriate pruning and mulching, also significantly contributes to tree health.
When necessary, chemical treatments can be a useful tool in the fight against a disease. However, if you’re unsure about what’s affecting your trees, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Remember, the effort you put into caring for your trees today will pay off in their health and beauty for years to come.

